BAE Systems has received a $247 million contract from the U.S. Space Force’s Space and Missile Systems Center to design and manufacture an advanced military GPS receiver and next-generation semiconductor.
BAE Systems has received a $247 million contract from the U.S. Space Force’s Space and Missile Systems Center to design and manufacture an advanced military GPS receiver and next-generation semiconductor.
The technology will provide positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) capabilities to warfighters so they can execute missions in challenging electromagnetic environments.
MGUE Increment 2
The contract is related to November’s U.S. Department of Defense contract for M-Code military GPS technology.
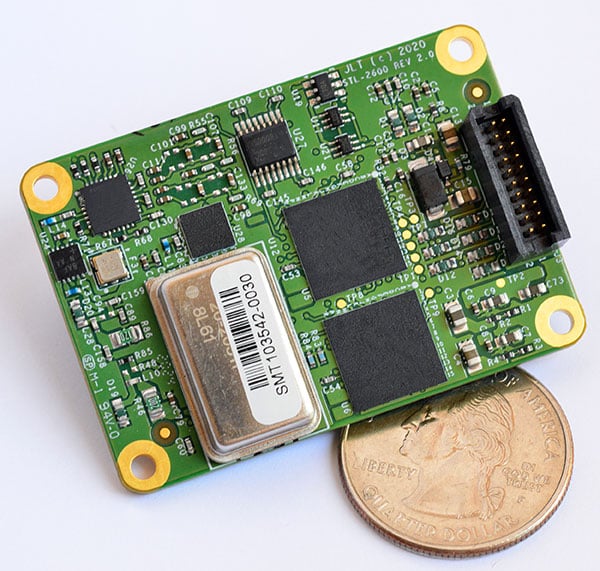
The Military GPS User Equipment (MGUE) Increment 2 Miniature Serial Interface program will provide improved capabilities for size-constrained and power-constrained military GPS applications, including precision-guided munitions and battery-powered handheld devices.
The program will focus on the certification of an advanced application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) and the development of an ultra-small, low-power GPS module.
Both products will work with the next-generation military M-code signal technology, which provides reliable GPS data with anti-jamming and anti-spoofing capabilities to protect against electronic warfare threats.
“This program enables us to further develop our core M-code technology to deliver high-performance, next-generation GPS capabilities,” said Greg Wild, director of Navigation and Sensor Systems at BAE Systems. “Our M-code receiver and next-gen ASIC will enable secure and reliable military GPS capabilities in a broader range of platforms.”
BAE Systems’ Precision Strike business has 45 years of military GPS experience and more than 1.5 million GPS devices on over 280 platforms around the world. The company is currently producing M-code GPS receivers in multiple form factors, including a low power, small form factor M-code solution.
Additional prototypes are in development for ground, weapons and airborne mission applications, and the company’s M-code GPS products are available to U.S. allies via foreign military sales.
Work on the program will be conducted at the company’s facility in Cedar Rapids, Iowa.