A roundup of recent products in the GNSS and inertial positioning industry from the December 2022 issue of GPS World magazine.
AUTONOMOUS
Flight Controller
Turns a UAV into a connected autonomous system

Photo: Auterion
Skynode reference-design hardware is built with Remote ID in mind, enabling UAV users to comply with the FCC rule Remote Identification of Unmanned Aircraft (Part 89). A built-in connectivity stack with 4G, Bluetooth and Wi-Fi enables automatic real-time data transmission from the UAV to the cloud. Built on open standards, Skynode is flexible and extensible, allowing users to leverage a variety of compatible software and hardware components. The connections enable automatic sending of logs, images and real-time video streams from the field to remote experts.
Auterion, auterion.com
Heavy-Lift UAV
Can carry 440-pound payload 25 miles

Photo: Volocopter
The VoloDrone is a fully electric, heavy-lift utility UAV with a range of up to 25 mi carrying a carrying a 440-lbs payload. The rotor area has a diameter of 30 ft, and the vehicle is 7.5 ft high. It can be remotely piloted or can fly autonomously on preset routes. Loads can be carried between the legs of the landing gear on standard rack mounts or slung below, or a tank and sprayer could be fitted for agricultural applications. The 18-rotor multicopter platform uses swappable lithium-ion batteries and an in-house flight control system, and benefits from existing development and test of the Volocopter air-taxi.
Volocopter, volocopter.com
Mapping UAV
Maps areas greater than 20,000 hectares

Photo: Boreal
With a wingspan of 4.20 m, the BOREAL NRM remotely piloted aircraft integrates efficient photogrammetry devices for mapping large areas, even in areas inaccessible to traditional mapping aircraft. Its flight-control system is designed for image-capture management and optimal coverage of areas greater than 20,000 ha. The BOREAL NRM offers an overall and precise view of cultivated areas (1 cm to 3 cm per pixel), simplifying crop monitoring and facilitating human intervention in places that require it (such as water stress, treatment of pests).
Boreal, www.boreal-uas.com
ISR System
Developed for the Spanish Ministry of Defense
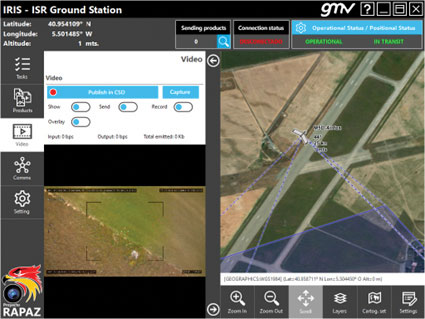
Photo: GMV
The IRIS unmanned vehicle command-and-control system provides intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) interoperability — essential aspects of any military operation. The IRIS system integrates unmanned vehicles with other command-and-control systems for monitoring and gathering information for a variety of operational scenarios. IRIS uses each unmanned vehicle’s own communication systems and 5G technology to provide situational awareness for decision makers before and during operations. A simplified interface allows integration of sensors and platforms into a command-and-control network, providing interoperability with other command, control, communication and computer ISR (C4ISR) systems. IRIS performed well during NATO’s REPMUS 22 (Robotic Experimentation and Prototyping Augmented by Maritime Unmanned Systems) exercise in September.
GMV, gmv.com
Docking Station
Sends UAVs to complete missions
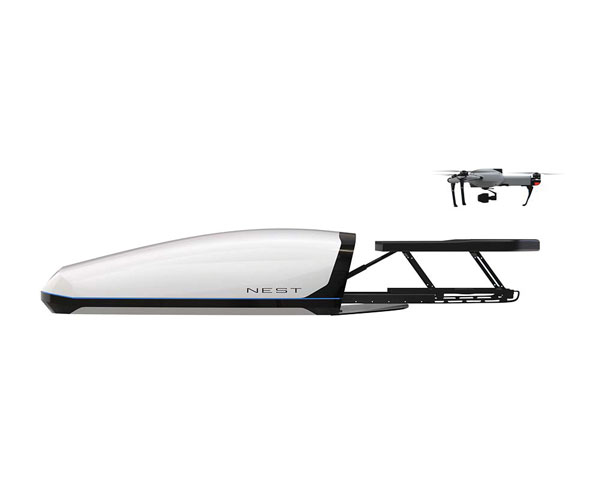

Photo: AtlasNest
The AtlasNEST UAV system features a docking station to provide fully autonomous 24/7 readiness for infrastructure inspections, emergency situations and security missions requiring shared situational awareness and management. Using the AtlasSTATION interface, an operator sets a target destination, and the lightweight UAV deploys in less than three minutes. Sending a drone to collect visual data and reveal possible problems can help prevent putting personnel in unsafe circumstances. AtlasNEST has built-in artificial-intelligence technologies, including autonomous battery swapping. Using the AtlasSDK, AtlasNEST can be incorporated into current security systems.
Atlas, atlasuas.com
Line Painter
Robot built to paint lines on athletic fields

Photo: Turf Tank
Turf Tank is an autonomous, GNSS-guided line-marking robot built specifically to paint lines on athletic fields. More than 550 Turf Tank robots are deployed across the United States, painting athletic fields at public schools, major colleges and universities, amateur and professional soccer clubs, local parks and recreation departments, and at two National Football League stadiums. The Turf Tank robots can paint a full soccer field in less than 30 minutes, compared to two or three hours for manual painting. Similarly, the robot can paint a football field in two or three hours compared to eight to 10 hours to paint a football field. The robots are eco-friendly — they’re powered by rechargeable batteries and use far less paint than most older paint machines.
Turf Tank, turftank.com
UAS Package
Takes users through project lifecycle

Photo: Autel Robotics
The Autel EVO II Pro Series combines Carlson’s software and hardware surveying and mapping solutions with a UAV from Autel Robotics. The Carlson suite is designed to take professionals throughout a project’s lifecycle: setting ground control points with the Carlson BRx7 GNSS receiver and RT4 data collector with SurvPC field software, the drone flight, PC photo and data processing, and creating finished plans in CAD.
Carlson Software, carlsonsw.com; Autel Robotics, autelrobotics.com
OEM
GPS Add-On Board
Provides PNT to design engineers
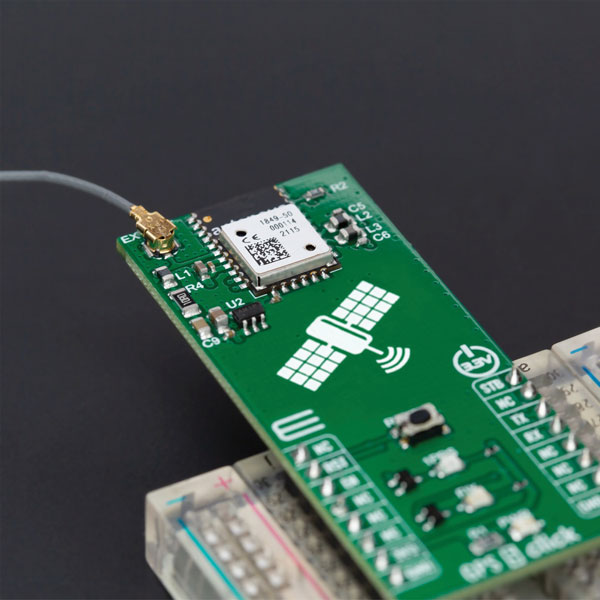
Photo: MikroElektronika
The GPS 5 Click is a compact add-on board that provides users with positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) services. The board features the M20050-1, a GPS module using the MediaTek MT3333 flash chip and an Antenova GNSS receiver for optimum performance. The receiver tracks three GNSS constellations concurrently (GPS + Galileo + GLONASS or GPS + Galileo + BeiDou) and has configurable low-power modes operating from a 3.3V power supply. In addition to the possibility of using an external antenna, backup power, and various visual indicators, the M20050-1 has an accurate 0.5 ppm TXCO ensuring short time-to-first-fix and multipath algorithms that improve position accuracy in urban environments.
MikroElektronika, mikroe.com
Timing Modules
Support for concurrent L1 and L5 reception
Photo: Furuno
Modules GT-100, GT-9001 and GT-90 are time-synchronization GNSS receiver modules compatible with all GNSS systems. The three modules deliver nanosecond precision for 5G mobile systems, radio communications systems, smart power grids and grandmaster clocks. Each suits different applications based on supported frequency bands and output signals. GT-100 supports concurrent L1 and L5 reception and delivers three outputs including 1 pulse per second (1 PPS) synchronized with UTC as well as user-programmable frequencies. The outputs can be set to 10 MHz, 2.048 MHz and 19.2 MHz, reducing time to market and saving costs through reduced component needs. GT-9001 supports L1 and delivers high-stability 1PPS and programmable clocks on three channels. GT-90 supports L1 and provides a 1 PPS high stability output. All models have time stability of 4.5 ns (1 sigma) and are equipped with multipath mitigation to minimize degradation of performance in urban areas.
Furuno Electric Co., furuno.com
Firmware Update
Adds QZSS CLAS to ZED-F9R GNSS module
Photo: u-blox
The latest firmware update for the u-blox ZED-F9R high-precision GNSS module adds support for Japan’s QZSS CLAS correction services (ZED-F9R-03B). The ZED-F9R also now supports u-blox SPARTN 2.0 correction data.
u-blox, u-blox.com
Smart Antenna
Has L-band, IP capability

Photo: Tallymatics
The TW5390 smart antenna has IP network and L-band augmentation service capability. Along with a Tallymatics antenna, it has a high-precision u-blox F9R GNSS receiver and DS9 L-band receiver modules. The combination delivers a reliable and convenient smart antenna yielding <6-cm accuracy, with precise point positioning/real-time kinematic (PPP/RTK) augmentation services via the PointPerfect subscription service. The antenna provides superior multipath rejection with Tallysman Accutenna technology, a low noise amplifier, Tallysman’s eXtended Filtering (XF) technology, which mitigates saturation from nearby RF signals (targeting LTE and Ligado), a tight, measured phase-center offset and low axial ratio, enabling accurate and precise positioning, direct decoding of PointPerfect, SPARTN formatted augmentation packets (u-blox specific)
Tallymatics, tallymatics.com
GNSS Modem
Tracking enables potential applications and projects

Photo: TE Connectivity
The Lembas LTE/GNSS USB modem provides plug-and-play GNSS tracking as well as LTE and CAT4 network connectivity via a robust USB interface to a variety of small-board computers utilizing the ARM chipset. Through a single-command setup process, users can have GNSS access to a wide variety of projects. The modem has been tested with Raspberry Pi Model B, Odroid XU4 and N2, ASUS Tinker Board, and NVIDIA Jetson Nano.
TE Connectivity, te.com
MACHINE CONTROL
Site Supervisor System
Base/rover system provides 3D grade control
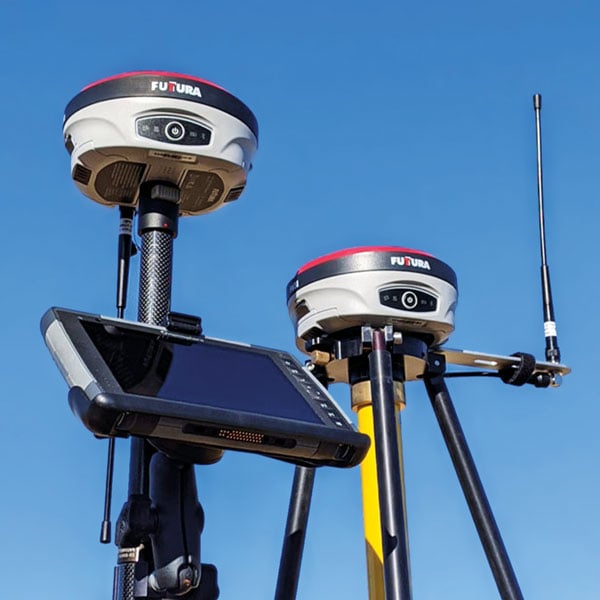

Photo: Futtura
The universal construction site supervisor system is designed to help contractors manage all their job site activities. It includes the SiteMetrix Grade and the multi-frequency, multi-GNSS F631 RTK base and rover. SiteMetrix is user friendly, easy to understand and portable. Contractors can use the Futtura system to localize sites, check grade, configure base stations, set stakes and calculate volumes of material removed. Users will see the benefit of seamlessly performing data collection and layout, all in one easy-to-use application, the company says. The F631 GNSS receiver is powered by SureFix RTK technology, which offers a real-time dual-solution point verification. The F631 GNSS receiver is powered by Hemisphere GNSS’ Athena RTK technology. With Athena, F631 provides state-of-the-art RTK performance when receiving corrections from a static base station or network RTK correction system. With multiple connectivity options, the F631 allows for RTK corrections to be received over radio, cell modem, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or serial connection. F631 delivers centimeter-level accuracy with virtually instantaneous initialization times and robustness in challenging environments.
Futtura, futturaus.com
Cab Displays
Provide connectivity for the field
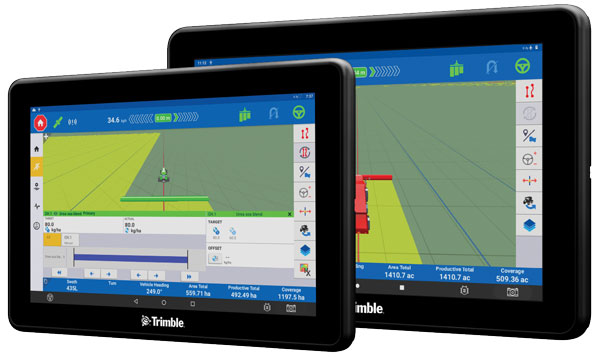
Photo: Trimble
The Trimble GFX-1060 and GFX-1260 next-generation displays for precision agriculture applications enable farmers to complete in-field operations quickly and efficiently while also mapping and monitoring field information in real time with precision. Both displays feature an Android-based operating system and enhanced processing power for controlling and executing in-field work. The new flagship GFX-1260 is a 12-in (30.5 cm) display, while the GFX-1060 is a 10-in (25.6 cm) display, and both are compatible with the Trimble NAV-500 and NAV-900 GNSS guidance controllers. The displays are ISOBUS-compatible, which allows one display or terminal to control ISOBUS implements, regardless of manufacturer. The displays enable farmers to set up and configure their equipment through Trimble’s Precision-IQ field software, including manual guidance, assisted and automated steering, application controls, mapping and data logging, equipment profiles and camera feeds from attached inputs and other internet-based apps.
Trimble, trimble.com
Retrofit Kit
Enables affordable smart construction upgrades for fleets

Photo: Komatsu
The Smart Construction Retrofit kit turns a conventional Komatsu excavator “smart” with 3D guidance and payload monitoring. With a kit installed, an operator is no longer required to set up a laser or bench every time the machine moves. The kit’s GNSS receiver determines where a machine is on the job site and what the target grade is. The need for additional labor is reduced because the technology collects and delivers information directly to the operator. Designed to improve grading performance and provide more time- and cost-management tools, Smart Construction Retrofit kits can bring 3D to most Komatsu excavators in a fleet. The kit gives operators the latest design data, measures payload volumes and load counts, and allows managers to monitor production from the office by integrating Smart Construction applications. The payload meter helps prevent overloading trucks by promoting proper loading weights for on- and off-road vehicles, to reduce the potential for equipment damage and other risks.
Komatsu, komatsu.com
Precision Guidance
Entry-level system for farmers
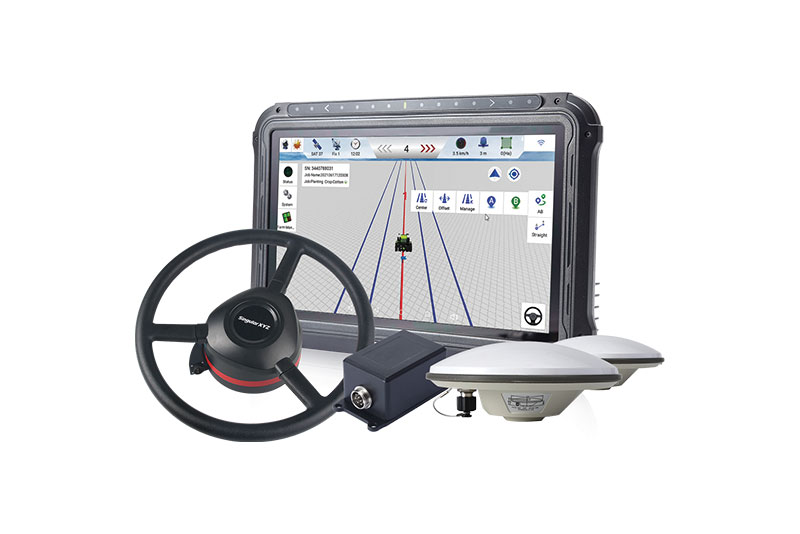

Photo: Singular XYZ
The SAgro10 GNSS is an upgradeable entry-level guidance system for precision agriculture, which can be easily upgraded to the SAgro100 automatic steering system. Equipped with a high-precision GNSS module, the SAgro10 tracks all constellations. For users with network coverage or a UHF base station, the SAgro10 system provides centimeter-level accuracy navigation in real-time kinematic mode. In the absence of base stations, it can still provide sub-meter navigation accuracy in single-point smoothing mode. The system is compatible with most agricultural tractors and can be installed in 15 minutes. It supports a 10-in sunlight-readable touchscreen with a clear graphic interface. The SAgro10 software can intelligently manage the work area and simplify user operations, such as recording the completed work area and planning the work route.
SingularXYZ, singularxyz.com
Gilla detta:
Gilla Laddar in …


























