In a first for any satellite navigation system, Galileo has achieved the first position fix based on navigation signals carrying authenticated data, according to the European Space Agency.
Galileo’s Open Service Navigation Message Authentication (OSNMA) is intended as a way to combat malicious spoofing of satnav signals.
OSNMA receivers successfully calculated an OSNMA-protected position fix after Galileo satellites started transmitting authentication data at 15:28 UTC on Nov. 18, 2020. The first tests used eight Galileo satellites for around two hours on Nov. 18. Tests have continued ever since, for intermittent periods, and will continue over the next months ahead of a public observation phase.
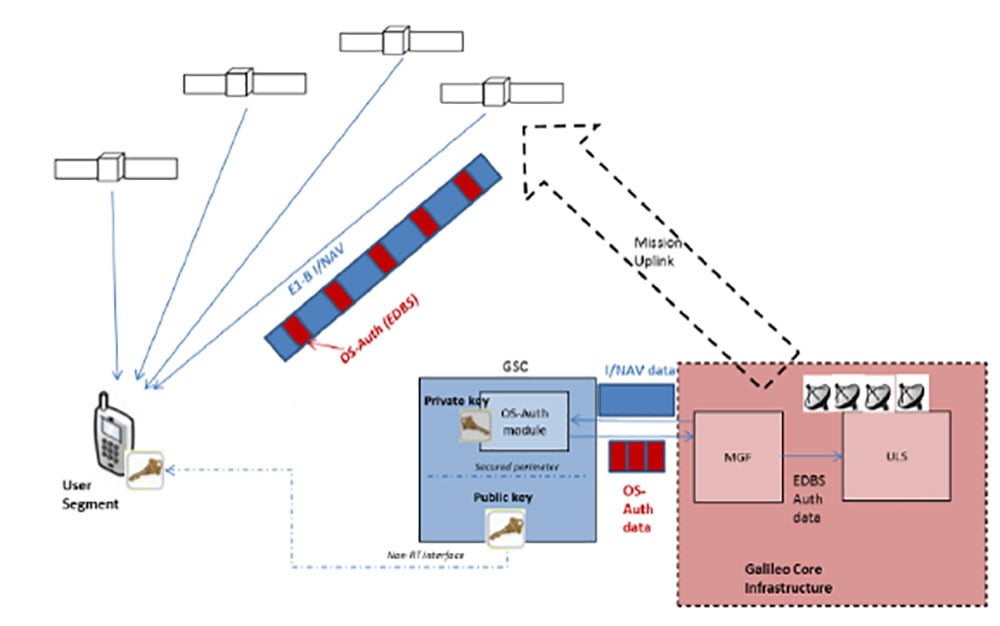
The first authenticated signal position, velocity and timing fixes were made using a total of eight Galileo satellites for around two hours on Nov. 18, 2020. The tests represent a first proof-of-concept for an eventual operational service offering positioning with authenticated data to users. (Image: ESA)
Pioneering a long-awaited service
The Galileo OSNMA authentication mechanism allows GNSS receivers to verify Galileo information, making sure that received data are indeed from Galileo and not modified in any way.
“Ensuring the validity of positions elaborated by GNSS is one of the main challenges before addressing an entirely new set of applications demanding dependability and resilience,” said Matthias Petschke, director of space at the European Commission, DG DEFIS. “Galileo is now set on course to deliver on this highly anticipated feature and has many more novel features in store for the coming years.”

Testing is taking place at ESA’s Navigation Laboratory at ESTEC in the Netherlands, the same site where the first Galileo positioning fix took place in 2013.(Photo: ESA)
Increased robustness
OSNMA test signals are being broadcast by the Galileo constellation using the spare bits from the current navigation message, therefore not impacting the legacy OS receivers implementing the current OS Signal-In-Space Interface Control Document (OS SIS ICD).
“Galileo’s Open Service Navigation Message Authentication is one of its key differentiators,” said Rodrigo da Costa, executive director of the European GNSS Agency. “The additional robustness that it will provide to the Galileo signal will be critical for many applications, particularly those where security and trustworthiness are a priority, making the OSNMA a key component in any resilient PNT solution.”
OSNMA works on a comparable basis to everyday encryption, where sending a digitally signed document involves both sender and recipient using compatible cryptographic keys (private and public) to validate the document’s source of origin.
“Up until now, as a navigation satellite disseminates navigation and timing data, there is no way of confirming these data are indeed coming from their apparent originator,” explained Paul Verhoef, director of navigation at the European Space Agency. “As a result, the data could be falsified, a phenomenon known as spoofing, where corrupt false signals mislead receivers about their position, misleading their users in turn, with potentially serious consequences.”
An ESA Navigation Directorate team at the ESTEC technical centre in the Netherlands worked with their European GNSS Agency (GSA) counterparts at the twin Galileo Control Centres in Italy and Germany and the Galileo Service Centre (GSC) in Spain to develop and test the OSNMA.
Next steps
Upon successful completion of the internal testing phase, a public observation phase will begin, in which the OSNMA signal will be publicly accessible. In preparation for this phase, the OSNMA user Signal-In-Space Interface Control Document (OSNMA SIS ICD), receiver implementation guidelines, and the necessary cryptographic materials will be published. This will allow receiver manufacturers and application developers to test and prepare their products.
During the public observation phase, feedback will be gathered from users, leading to the consolidation of the service.