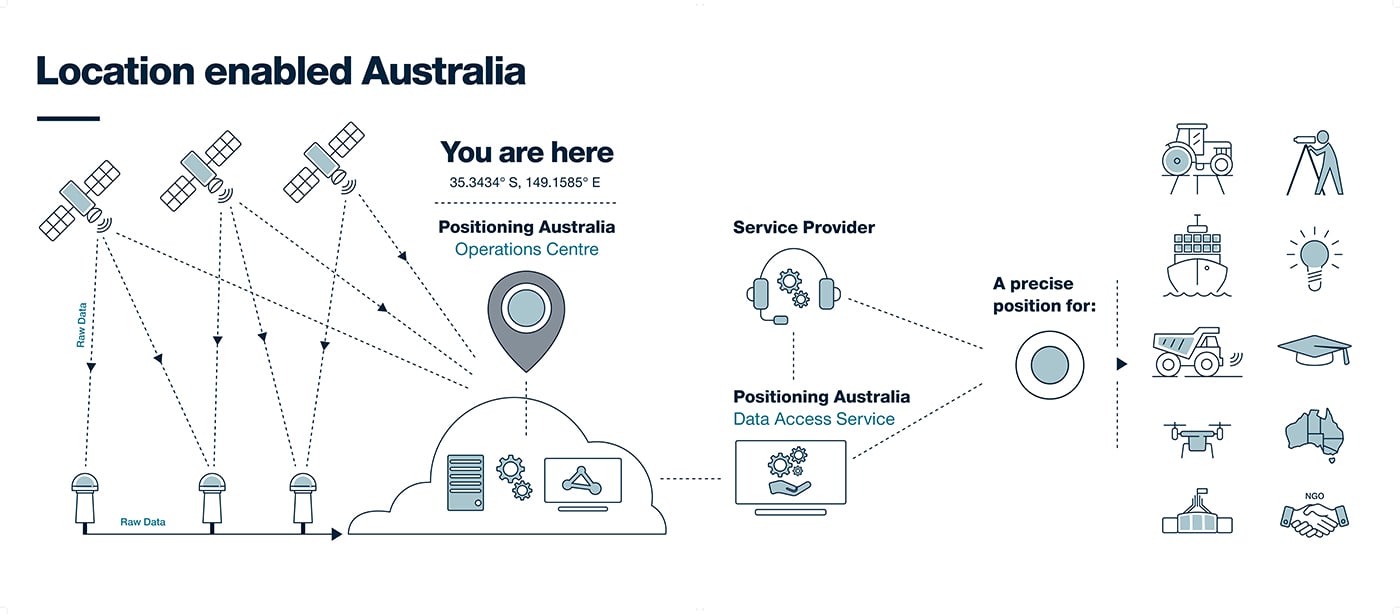
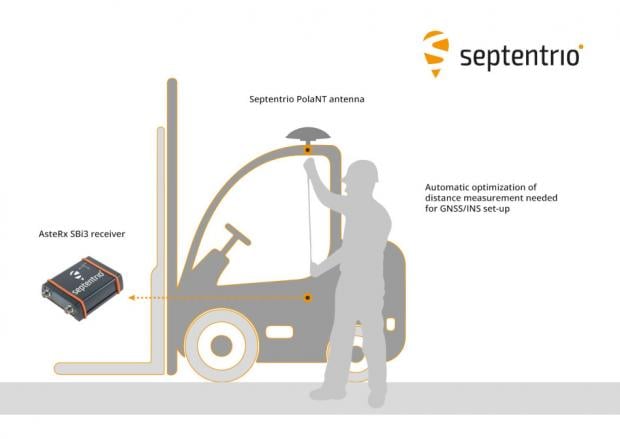
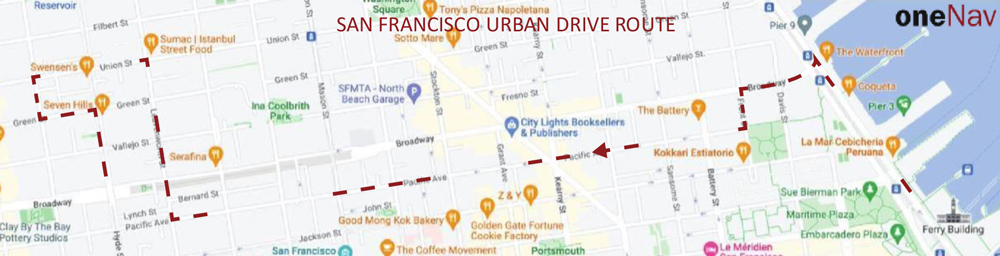
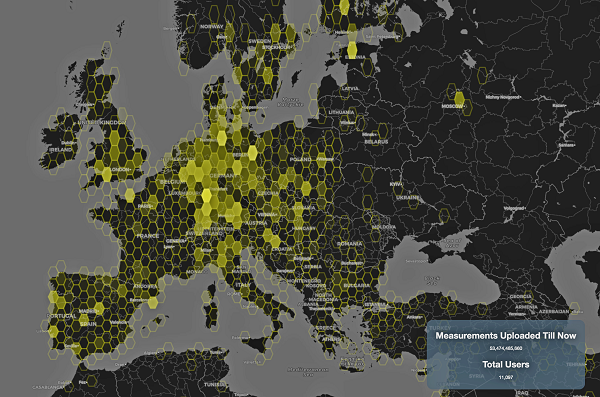
The INTERGEO Expo & Conference focuses on innovations for a smarter world. INTERGEO 2022 will take place October 18-20 in Essen, Germany.
Topics including the importance of geoinformation for internal security, monitoring for disaster control and prevention, open data, digital twins alongside their use in construction and housing, mobility, sustainability and climate change, BIM and engineering applications with UAV, laser scanning and monitoring will be discussed during the 2022 event.
Additionally, the outdoor area of Messe Essen will show live demonstrations of the latest UAV applications in surveying, agriculture, construction, security and many more.
According to INTERGEO organizers, 300 international companies are already registered at the Expo, from innovative young start-ups to international key players such as Autodesk, Esri Inc., Hexagon, Trimble, Topcon and many more. The organizers expect around 500 exhibitors by October.
“All the international key players in the industry will be there.There was no doubt about it – they all want to get back to their customers, to visitors, to the live atmosphere and the power of meetings”, says Prof. Dr-Ing. Hansjörg Kutterer, President of the organiser DVW e.V., Association for Geodesy, Geoinformation and Land Management.
For those who are unable to attend the event in Germany, there will be some opportunities to participate in the Expo remotely.
Up close and personal
Digital Twins will receive their big break at the Conference 2022. Their use in building information modeling, smart planning and construction as well as mobility will be the focus of the event. Digital twins will be used to further development of urban data platforms in the context of smart cities and their variety of applications, as well as the use of smart city solutions in terms of innovation and sustainability and a basis for predictions and scenarios in the event of disasters.
The main topics in 2022 are Digital Twins and their value creation, 4D geodata and Geospatial IoT, potentials of remote sensing, BIM 4.0, industrial surveying, measurement systems and robotics, smart cities and mobility in the context of climate change and sustainability, mobile mapping, web services and GeoIT in disaster relief, spatial reference and positioning, earth observation and Galileo.
Hansjörg Kutterer points out the high innovative power of the industry: “We are experiencing high dynamics in segments such as mobility, environment and sustainability, climate protection and urbanization. Geo-IT has positioned itself as a solution provider for these topics. Problem-solving without Geo-IT is unthinkable in these subject areas. Come to Essen on the 18th to 20th of October and visit Intergeo Expo and Conference.”
How to attend
Tickets for INTERGEO are now available. An early-bird registration rate is available until August 31. Tickets can be found at https://www.intergeo.de/en/tickets.
Registration for new exhibitors is open as well. All information, such as application procedures and funding amounts, can be found on the INTERGEO website at www.intergeo.de/en/.